Cellular respiration is an exergonic process of gaining energy from organic compounds by steps. The process of using oxygen is called aerobic cellular respiration, and the process of not using oxygen is known as anaerobic cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a complex sequence of chemical reactions, but the overall equation is simple:
Three overall goals of the process:
1. To break the bonds between the six carbon atoms of glucose, resulting in six carbon dioxide molecules.
2. To move hydrogen atom electrons from glucose to oxygen, forming six water molecules.
3. To trap as much of the free energy released in the process as possible in the form of ATP.
Four stages of the process:
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate oxidation
3. The Krebs Cycle (citric acid cycle)
4. Electron transport and chemiosmosis.
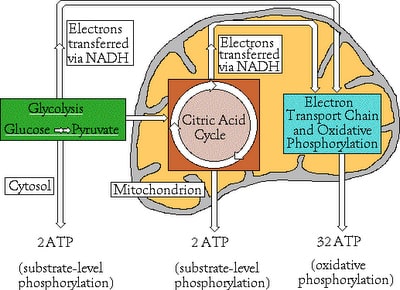
There are two methods to generate energy that produced during the cellular respiration:
1. Substrate-level phosphorylation:
It is a mechanism to form ATP directly in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by transferring a phosphate group directly to ADP from a phosphate-containing compound (anaerobic).

For each glucose molecule processed, 4 ATP molecules are generated this way in glycolysis and 2 in the Krebs cycle.
2. Oxidative phosphorylation:
It is a mechanism to form ATP indirectly through a series of enzyme-catalyzed redox reactions involving oxygen as the final electron acceptor (aerobic).
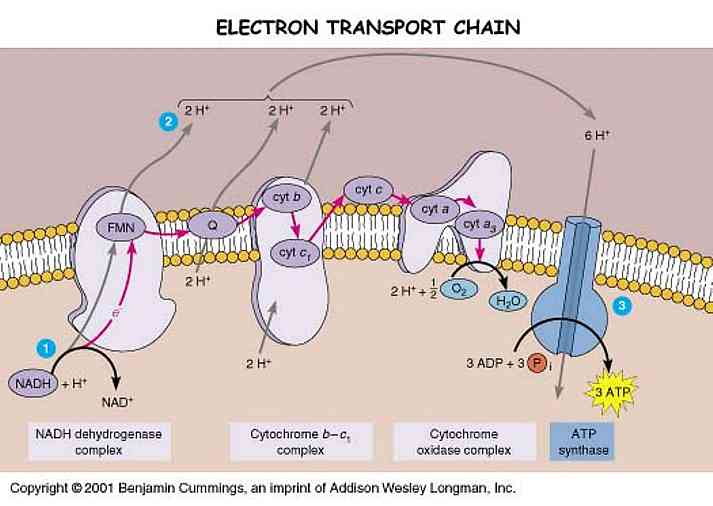
1) The coenzyme NAD+ accepts two electrons and one proton from a portion of the original glucose molecule, and reducing to NADH. A dehydrogenase enzyme is used to catalyze this reaction.
NAD+ reduction occurs in one reaction of glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation step, and in three reactions of the Krebs cycle.
2) The coenzyme FAD is also reduced to FADH2 by accepting two hydrogen atoms (two protons and two electrons).
FAD reduction occurs in one of the reactions of the Krebs cycle.
The reduced coenzymes act as mobile energy carriers within the cell, moving free energy from one place to another and from one molecule to another (a cell transfers free energy from NADH and FADH2 to ATP). It involves the last stage of the cellular respiration process by using of free oxygen molecules: electron transport and chemiosmosis.
没有评论:
发表评论